Multimodal characterization of pediatric patients with neuromuscular diseases in southwestern Colombia.

DOI:
https://doi.org/10.37980/im.journal.ggcl.20242348Keywords:
Spinal Muscular Atrophy, Duchenne muscular dystrophy, big data, early diagnosis, precision medicineAbstract
Introduction: Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy (DMD) and Spinal Muscular Atrophy (SMA) are rare but severe genetic neuromuscular diseases in the pediatric population with high burden of morbidity and mortality. Despite advances in their understanding and search for targeted therapeutic options, there are still gaps in timely detection, characterization, patient follow-up, active search for carriers and in some Latin American countries no neonatal screening. Objective: To characterize clinically, paraclinically, imaging and molecularly patients with presumptive and confirmed diagnosis of Duchenne muscular dystrophy (DMD) and Spinal Muscular Atrophy (SMA) attended in a pediatric center of reference and excellence in Southwestern Colombia. Materials and Methods: Observational cross-sectional study in patients under 18 years of age with ICD-10 diagnoses related to DMD and SMA. Data were exported to an Excel matrix in Office 365 version 2403, and then to IBM SPSS version 29 to perform a univariate analysis, measures of central tendency and dispersion were used for numerical variables, considering their distribution, and absolute frequencies and percentages for qualitative variables. Results: After reviewing 954 medical records belonging to a pediatric care center in Southwestern Colombia between 2015 - 2021, 422 cases related to Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy (DMD) and Spinal Muscular Atrophy (SMA) were identified; excluding duplicates and unrelated records, from these, 99 cases were randomly selected for a comprehensive analysis using OpenEpi version 3.01, distributed in two groups: SMA (n=23) and DMD (n=76). Patients confirmed with Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy (DMD) showed symptom onset at 54.5 ± 29.0 months and diagnosis at 98.8 ± 34.9 months, being more common in males with hypotonia and elevated creatin kinase (CK) levels, 54.5% had cognitive impairment and 88. 2% had family history, in Spinal Muscular Atrophy (SMA), the onset of symptoms was at 28.9 ± 37.7 months and diagnosis at 37.9 ± 38.2 months, being predominant in females with areflexia and fasciculations, there were no records of cognitive function in confirmed patients, and 21.7% had family history of SMA, in addition to slight elevations of CK. In the SMA group, 9 cases were molecularly confirmed and 3 were supported by medical records; in contrast, in the DMD group, 22 cases had molecular confirmation, but 9 had annotations in medical records, although these reports were incomplete. Conclusions: Early suspicion and diagnosis of these progressive neurodegenerative diseases characterized by high morbidity and mortality rates is critical to impact the holistic approach patients should receive. Given the continuous advance in diagnostic methods and innovative and targeted therapeutic options (hyperpersonalization medicine), it is necessary to create complete medical-clinical registries and "big data", which have all the current tools available (multimodal diagnostic options) to facilitate patient re-contact, follow-up and to be able to offer personalized, precision care that improves the quality of life of patients and their families, contributing to the generation of integrated and targeted public policies.
INTRODUCTION
Hereditary and acquired neuromuscular diseases affect the entire population from childhood to late adulthood, although they are classified as rare diseases due to their low individual prevalence, they can manifest in acute presentations, although they are generally chronic and have a stable or progressive course. They constitute a group of more than 150 diseases that affect any of the components of the motor unit, that is, the functional unit constituted by the body of the anterior horn motoneuron of the spinal cord, its axon (peripheral nerve), the neuromuscular junction, and all muscle fibers innervated by this motoneuron. The final effector of this system is the muscle, but it can be compromised either primarily or secondarily to denervation.According to this concept, NM diseases can be classified into: Motor neuron and nerve diseases (neuropathies), myopathies or primary muscle diseases without structural alterations in the peripheral nerve, and disorders of the neuromuscular junction.
In a few years, we have gone from a classification based on histopathological and clinical features to one in which molecular features are the ones that articulate the organization of the different groups, with clinical features allowing for the establishment of subgroups within a group with a common genetic disorder. Currently, classification based on molecular biology is of interest, allowing for the creation of new subtypes within the same set of symptoms.In this sense, Duchenne muscular dystrophy is part of the group of dystrophinopathies, it is one of the most common muscular dystrophies and affects more than two hundred thousand people worldwide [3]. The risk of recurrence in a carrier woman of the disease in each pregnancy is: 50% of sick children, 50% of healthy children; 50% of carrier daughters and finally 50% of non-carrier daughters although 30% of patients present de novo variants [4]; in any case, this is the result of alterations in the dystrophin gene (DMD), located in the Xp21 locus, the variants of this gene cause a progressive muscle degeneration due to the absence of an essential protein for the structural stability of the muscles [5].Duchenne muscular dystrophy has a prevalence of 1 in 5,000 live-born males [6], it is extremely rare in female patients however this variability in the expression of the disease in carrier women can be explained by the process of random X chromosome inactivation, also known as Lyonization [7], in this process, one of the two copies of the X chromosome in women is randomly inactivated in each cell of the body, which can influence the severity of the symptoms presented.
Despite extensive research efforts, finding a cure for DMD remains a significant challenge, highlighting the importance of exploring new treatment approaches [8]. Therefore, it is crucial to consider advanced therapies, such as gene therapy, cell therapy and immunotherapy, which could address the disease at its origin, these include gene transfer or implantation, exon skipping and genetic editing.
There is a growing demand for new therapies capable of significantly improving the treatment of a wide range of patients; advances in genetic reprogramming have enabled the development of AAV vectors (Adeno-Associated Viruses) to deliver specific therapies.
Recently, the FDA (Food and Drug Administration) approved a new oral medication called Duvyzat (givinostat), designed for patients 6 years and older with DMD [25]. Likewise, the biogenesis of exosomes can be directed to transport components of gene editing or specific therapies to particular tissues or cell types, such as the brain and muscle [9].
This targeted pharmacological approach has the potential to restore muscle function and significantly improve the quality of life of affected patients, therefore, it is crucial to perform multimodal diagnostic confirmation including molecular studies, follow-up, and have complete clinical big data and the ability to recontact patients to continuously inform them of diagnostic and therapeutic advances, provide preventive measures and interventions that reduce the expression of the medical condition impacting its natural history.
On the other hand, Spinal Muscular Atrophy (SMA) is an inherited disease that affects the cells of the anterior horn of the spinal cord, causing progressive weakness in proximal muscles.This condition, with autosomal recessive inheritance, affects both men and women equally, requiring the presence of two copies of the gene, one from each parent, for its manifestation; the probability that these parents will have an affected son or daughter is 25% in each pregnancy [11]. The estimated prevalence of SMA is around 1 case per 10,000 newborns according to studies in the general population. The classic form of the disease is the result of a variant in the genes that encode the survival motor neuron protein (SMN1 and SMN2), located on the long arm of chromosome 5, and is part of an inverted 500 kb duplication on chromosome 5q13. This duplicated region contains, at least, four genes and repetitive elements that make it prone to rearrangements and deletions [12].
During the last decade, Spinal Muscular Atrophy (SMA) has experienced significant changes thanks to advances in medical care and the development of specific treatments for this disease. In Spain, there is "RegistrAME", a registry of specific diseases that collects data on patients with SMA since 2015 [13]. This registry includes demographic and clinical information, as well as results reported by the patients themselves, which is essential for better understanding the disease and improving the quality of life of those affected. This approach could be extrapolated to less privileged populations in order to collect data on a large scale and contribute to improving the management of family expectations, appropriate disease management and patient needs, as well as a better understanding of the impact of the disease. Additionally, it can help monitor the evolution of care, resulting in the need for updated guidelines.
Taking into account the above-mentioned and the importance of implementing similar strategies in our country, this retrospective, observational cross-sectional study characterizing pediatric patients with suspected and confirmed Duchenne muscular dystrophy and spinal muscular atrophy was carried out in a reference pediatric institution in the Colombian Southwest through the analysis of big data from medical records between the years 2015 and 2021.This study sought to characteristically and multimodally characterize the selected patients in order to collect this information, to be able to generate its own record taking into account the continuous advance in diagnostic methods and innovative and targeted therapeutic options (hyperpersonalization medicine) and to be able to follow up, re-contact patients and offer them personalized, precise care that improves their quality of life, their families, contributing to the generation of integrated and targeted public policies.
MATERIALS AND METHODS
A retrospective observational cross-sectional study was conducted, reviewing electronic Big Data medical records from January 1, 2015, to December 2021 of patients under 18 years of age belonging to a pediatric reference center in southwestern Colombia. The aim was to characterize clinically, paraclinically, imaging and molecularly patients with suspected and confirmed Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy (DMD) and Spinal Muscular Atrophy (SMA).954 medical records with ICD-10 diagnoses related to neuromuscular diseases were analyzed, such as G710 (Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy), G120 (Proximal Spinal Muscular Atrophy), G120 (Autosomal Dominant Proximal Spinal Muscular Atrophy), G121 (Proximal Spinal Muscular Atrophy Type 2, Type 3, Type 4), and G122 (Other Unspecified Spinal Muscular Atrophies). Subsequently, 532 duplicate or non-related medical records were eliminated from those associated with the suspicion or confirmation diagnosis of DMD and SMA, leaving 422 records. A random selection calculation was performed using the OpenEpi version 3.01 program, obtaining 202 records after applying selection criteria. 103 medical records were excluded, resulting in a final sample of 99 medical records of children with suspicion and molecular confirmation of Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy and Spinal Muscular Atrophy, which were divided into two groups: 23 patients suspected of SMA and 76 of DMD.These patients were seen in the outpatient department of a pediatric institution in the city of Cali, in southwestern Colombia. The study was approved by the institution's ethics committee.
The data were recorded in a form that included all clinical, paraclinical, imaging, and molecular variables used for characterization. Data was systematized in a validated form filled out directly by one of the authors and exported to an Excel office 365 Version 2403 matrix. A spreadsheet was then exported to the IBM SPSS program version 29, and a univariate analysis was performed after evaluation through exploratory analysis. Measures of central tendency and dispersion were used for numerical variables according to their distribution, and absolute frequencies and percentages were used for qualitative variables.
RESULTS
During the study period (years 2015 - 2021), 954 patients consulted the outpatient service of a pediatric institution in the city of Cali - Colombia. After applying the selection criteria and eliminating repeated data, 99 patients were included, divided into two main groups: those with suspicion and confirmation of Spinal Muscular Atrophy (SMA) and those with suspicion and confirmation of Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy (DMD) (Figure 1).
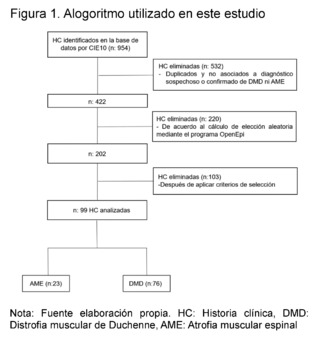
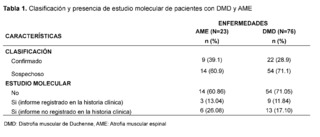
In the SMA group, 23 patients were identified, of which 9 patients were registered with a confirmed diagnosis through molecular studies, and 3 of them had records of these results in their medical records. In contrast, in the DMD group, 76 patients were found, with 22 patients having molecular confirmation, but only 9 of them had notes on the test results (Table 1).
The age at the time of evaluation, measured in months, was 58 for patients with suspicion and confirmation of Spinal Muscular Atrophy (SMA), while for those with suspicion and confirmation of Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy (DMD), the average age was 113.17 months; a greater predominance of affected males was evidenced in the DMD group, while in the SMA group a higher frequency in females was observed; the socioeconomic stratum with the highest number of patients was low stratum (stratum 2) with 21 cases (91.3%) for SMA and 72 cases (94.3%) for DMD. Regarding the health insurance regime, a higher frequency of care was recorded in the subsidized regime compared to the contributory regime, the patients who consulted the most mainly came from rural areas, with 13 cases (56.5%) for SMA and 49 cases (64.5%) for DMD. As for schooling, 15 cases (65.3% de casos en el grupo de DMD.
Regarding schooling, 15 cases (65.2%) in the SMA group were not attending school, while 39 cases (51.3%) in the DMD group were attending basic primary education (Table 2).
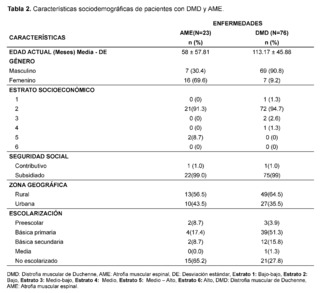
Table 3 presents the clinical and paraclinical characteristics observed in the suspected patients of the study sample. It was found that the mean age of symptom onset, expressed in months, was 21.17 ± 28.37 for patients with suspected and confirmed Spinal Muscular Atrophy (SMA), while for the Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy (DMD) group it was 54. 93 ± 29.11, muscle weakness was manifested in all cases, with an earlier onset in patients with suspected and confirmed SMA, measured in months 17.83 ± 26.50 compared to the DMD group 55.29 ± 29.36.
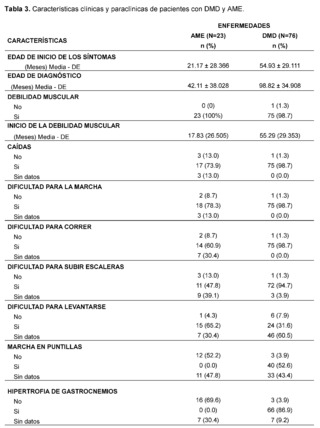
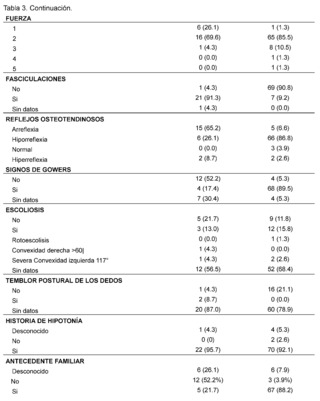
In addition, gait compromise was observed in both groups, representing 78.3% in patients with suspected and confirmed SMA and 98.7% in patients with suspected and confirmed DMD with the presence of falls in 73.9% in the SMA group and 98.7% in patients in the DMD group, difficulty in running was recorded in 60. 9% of confirmed and suspected SMA patients and 98.7% in patients in the DMD group, as well as difficulty climbing stairs in patients with suspicion and confirmation of both pathologies of lower frequency with 47.8% in the SMA group while 94. 7% in the DMD group, difficulty in getting up is described in patients with suspected and confirmed SMA in 65.2%, while it is less frequently recorded in 31.6% of patients in the DMD group, tiptoe walking was recorded in patients with suspected and confirmed DMD in 52. 6%, while it was not described in 52.2% of patients in the SMA group, likewise, the presence of hypertrophy of the gastrocnemius muscles was more frequent in the DMD group, with 86.9% of cases, and it was not described in 69.6% of the evaluated histories of patients with suspected or confirmed SMA.
As for the evaluation of muscle strength, this was affected in both pathologies, representing 69.6% of patients in the SMA group and 85.5% of patients with suspected and confirmed DMD classified as grade 2, on the other hand the presence of fasciculations was predominantly observed in patients with suspected and confirmed SMA, representing 91.3% of patients, and not found in 90. 8% of the DMD group, osteotendinous reflexes were compromised in both groups, with the presence of areflexia in 65.2% of patients in the SMA group and hyporeflexia in 86.8% of patients with suspected and confirmed DMD, on the other hand, Gowers' sign was more frequent in 89.5% of patients with suspected or confirmed DMD and was not found in 52.2% of patients with suspected or confirmed SMA. The presence of scoliosis was not described in the majority of patients in both groups 68.4% in DMD and 56.5% in patients in the SMA group as was postural tremor of the fingers where there was no data in 78.9% of the DMD group of patients and 87% in the SMA group of patients.
The presence of a history of hypotonia was found in both groups analyzed, with 92.1% for the DMD group and 95.7% for SMA. On the other hand, it was observed that most of the suspected and confirmed cases of patients with Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy (DMD) had a family history, with 88.2%, while, in contrast, patients in the Spinal Muscular Atrophy (SMA) group had no family history in 52.2% of the cases.
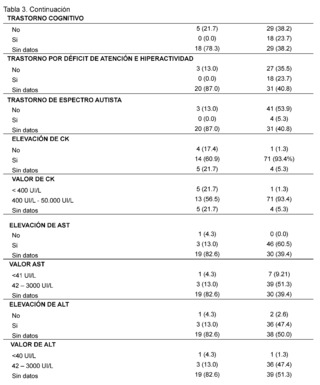
In the assessment of cognitive and neurodevelopmental involvement in the patients included it was found that in 38.2% no record of cognitive disorder was found in the group of patients with suspected and confirmed diagnosis of DMD, it is reported in 23.7% of patients included in the study, similarly, in the group of SMA patients represented with 78. 3% there is no data of cognitive disorder also for attention deficit hyperactivity disorder in 87% of patients with suspected and confirmed Spinal Muscular Atrophy (SMA), and no data found in 40.8% of patients in the DMD group, absence of autism spectrum disorder is described in 53.9% of patients with suspected and confirmed DMD and no data of it in 87% of the histories of patients evaluated for SMA.
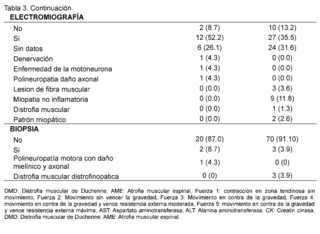
On the other hand, significant elevation of creatine kinase is observed being more evident in patients with suspected and confirmed DMD in 93.4% in contrast to the AME group representing 60.9% with values reaching a remarkably high range of 400 IU/L to 50,000 IU/L described in 93.4% in the group of suspected and confirmed DMD patients and in 56. 5% in the group of AME patients; AST levels between 42 IU/L and 3000 IU/L are described in patients with suspected and confirmed DMD, expressing 51.3%, no information of this variable was found in patients of the AME group in 82.6%, as for ALT elevation in the DMD group levels of 42 - 3000 IU/L were found in 47.4% of patients and only in 13% of patients included in the AME group. In the neuro conduction analysis (electromyography), the presence of non-inflammatory myopathy was detected in 11.8% of the patients in the group diagnosed with Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy (DMD), on the other hand, in the group of patients with Spinal Muscular Atrophy (SMA), signs of denervation, polyneuropathy with axonal damage and muscle fiber lesion were identified representing 4. 3% for each of them, in addition, biopsy reports with dystrophinopathic muscular dystrophy were found in 3.9% of patients in the DMD group, while 4.3% of biopsy reports of patients in the SMA group showed motor polyneuropathy with myelin and axonal damage.
The clinical, paraclinical and molecular characteristics of the patients with molecular confirmation of Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy are also detailed (Table 4). Age at evaluation, measured in months, was 130 ± 47.0, with an age at symptom onset of 54.5 ± 29.0 and an age at diagnosis of 98.8 ±34.9. All patients were male, with 20 of 22 belonging to socioeconomic stratum 2 and 2 of 22 to stratum 3, all being beneficiaries of the subsidized regime. Of these, 17/22 lived in rural areas and 5/22 in urban areas and, finally, 15/22 patients were attending primary school, while 7/22 were not in school.
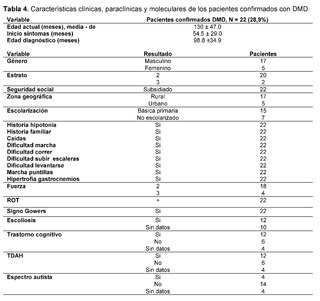
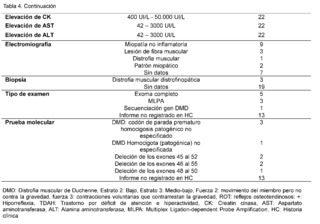
All patients had a family history of Duchenne muscular dystrophy, as well as a history of hypotonia, falls, difficulty walking, running, climbing stairs, getting up, tiptoe walking, and calf hypertrophy. Muscle strength was categorized as level 2 (movement of limb, but not against gravity) in 18/22 patients and level 3 (voluntary contractions that counteract gravity) in 4/18 patients. Osteotendinous reflexes, recorded as + (hyporeflexia), were present in all confirmed DMD patients. Gowers sign was observed in all 22 patients, while scoliosis was described in 12 of them.Additionally, cognitive impairment was registered in 12 patients, attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) in the same amount, and less frequently, the autistic spectrum was found in 4 out of 22 patients.
Levels of creatine kinase (CK) were observed between 400 IU/L and 50,000 IU/L in all cases (22/22), furthermore, elevation of alanine aminotransferase (ALT) and aspartate aminotransferase (AST) was evidenced in ranges between 42 IU/L and 3,000 IU/L.Regarding neuroconduction studies (electromyography), non-inflammatory myopathy was described in 9 out of 22 cases, muscle fiber injury in 3 out of 22, muscular dystrophy in 1 out of 22, myopathic pattern in 2 out of 22, and no findings were recorded in 7 out of 22 patients. As for the biopsy records, dystrophinopathic muscular dystrophy was found in 3 out of 22 patients. Finally, in terms of the molecular testing results recorded in the clinical history, 5 out of 9 patients reported genetic confirmation through complete exome sequencing, 3 out of 9 through Multiplex Ligation-dependent Probe Amplification (MLPA), and 1 out of 9 through sequencing of the specific DMD gene. Among the types of alterations reported were: 3 cases of pathogenic unspecified premature stop codon in hemizygous form, 2 cases of deletion of exons 45 to 52, 2 cases of deletion of exons 46 to 55, 1 case of deletion of exons 48 to 50, and 1 case of homozygous DMD.Unspecified pathogenic.
Regarding the clinical, paraclinical, and molecular characteristics of patients with a confirmed diagnosis of Spinal Muscular Atrophy (SMA) (Table 5). The age at the time of evaluation, measured in months, was 46.3 ± 47.4, with symptom onset at 28.9 ± 37.7 months and a diagnosis made at 37.9 ± 38.2 months. SMA was more frequent in males, with 6/9 patients, all patients belonged to stratum 2 with a subsidized health regimen. In terms of geographical origin, 7/9 patients came from rural areas and were not attending school, all had a history of hypotonia, no family history of the disease was recorded in any of the cases, some patients reported falls (3/9) and difficulty walking (4/9), while others did not have records of these data, difficulty running was not reported in most evaluated medical records (7/9).Muscle strength was classified as level 2 in most patients (5/9), and the presence of fasciculations was described in all cases, osteotendinous reflexes were classified as 0 (areflexia), and no data were found on scoliosis in 5/9 patients. As for cognitive disorders, it was not reported in most patients (5/9), as well as for attention deficit hyperactivity disorder (ADHD) and autism spectrum disorder, for which no data were found in any of the patients.
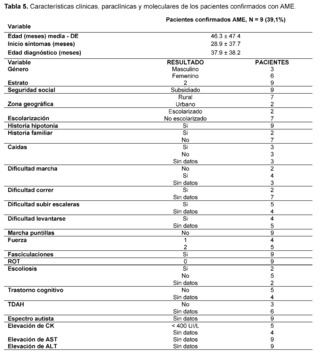
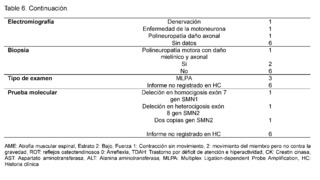
Elevation of creatine kinase (CK) was found with levels below 400 IU/L in 5/9 patients, with no recorded data of levels of aspartate aminotransferase (AST) and alanine aminotransferase (ALT); as for electromyography, denervation was described in 1/9 patients, motor neuron disease in another, and polyneuropathy with axonal damage in a third, with no recorded data for 6/9 patients.The biopsy report describes motor polyneuropathy with myelinic and axonal damage in 1/9 patients, while 6/9 did not have a biopsy record; regarding molecular confirmation, MLPA probe amplification was performed on 3/9 patients, while the molecular test result was not recorded in the medical history for diagnostic confirmation in 6/9 patients. Homozygous deletion of exon 7 of the SMN1 gene was described in one patient, heterozygous deletion of exon 8 of the SMN2 gene in another patient, and two copies of the SMN2 gene in a third patient, with no description of the test in 6/9 confirmed patients.
Elevation of creatine kinase (CK) was reported, with levels below <400 IU/L, without evidence of elevation of ALT or AST enzymes; concerning electromyography results, motor neuron disease was found in 1/3 patients, polyneuropathy with axonal damage in 1/3, and denervation in the last patient.The biopsy report revealed a motor polyneuropathy with myelinic and axonal damage in 1/3 patients, while no specific data were recorded in the other 2 cases.
<<DISCUSSION>>
This study is an observational cross-sectional analysis focused on neuromuscular diseases, specifically Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy (DMD) and Spinal Muscular Atrophy (SMA). The database comes from patients with suspicion and confirmation of SMA and DMD, representing the first documented registry in southwestern Colombia and in the referring institution where the data was collected between the years 2015 to 2021.
After evaluating 954 patients with ICD-10 codes for neuromuscular diseases, we selected 99 patients after applying specific criteria. Of these, 23 (23.2%) had suspicion of Spinal Muscular Atrophy (SMA) and 76 (76.7%) of Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy (DMD). Molecular confirmation showed that 9/23 (39.1%) cases of SMA and 22/76 (28.9%) cases of DMD were confirmed.
Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy (DMD) is a recessive X-linked disease. This implies that the risk of recurrence in a carrier woman is 50% for sick children and 50% for healthy children. Diagnosis in a family requires identifying carrier women in order to offer adequate genetic counseling. The prevalence of the disease is 1 in 5,000 male newborns [6].
Early diagnosis of Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy (DMD) is crucial to prevent serious complications. In this study, it was observed that the age of symptom onset in confirmed DMD patients was 54.5 ± 29.0 months, while the age at diagnosis was 98.8 ± 34.9 months. Previous studies by Crisafulli et al. [14], Salas et al. [15], Eslava Otálora et al. [16], and Li et al. [17] support the importance of early diagnosis, highlighting the early onset of the disease during childhood.The continuous need to improve early detection of signs and symptoms of DMD is emphasized, especially through monitoring psychomotor development.
Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy (DMD) mainly affects males due to a single altered copy of the gene on their X chromosome, while carrier females, who have one altered copy, usually do not present severe symptoms [18].
According to our study, 77.2% of confirmed cases of DMD were males, while 22.7% were females, which can be explained by the process of random X chromosome inactivation, known as lyonization [7]. This process of random inactivation of one copy of the X chromosome in females may influence the severity of the symptoms presented.In our study, after evaluating factors such as socioeconomic status, social security, geographic location, and educational level, we decided to focus on birthplace rather than medical care site, given the difficulty of access to health services in certain areas of the country.
We observed that the majority of patients belonged to the low stratum (Stratum 2), representing 90.9% of confirmed cases and 94.7% of the total patients. All confirmed patients and 99% of the total were affiliated with the subsidized regime. In terms of geographic location, 77.2% of confirmed patients and 64% of the total came from rural areas. Additionally, 68% of confirmed patients were attending primary education, with this percentage being 51% for the total patients with Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy (DMD). Rangel et al.2012 [19] suggests that dystrophinopathy is panethnic, implying a distribution of patients in all regions of the country. On the other hand, Eslava Otálora et al. 2016 [16] analyzed data from 99 patients between 2006 and 2015 at the IPS Quinta Mutis of the Universidad del Rosario (Bogotá), taking into account their place of birth to see their distribution. Their study revealed that 31.31% of the total patients diagnosed with DMD were concentrated in Bogotá.
Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy (DMD) is a disease that causes significant disability due to muscle weakness, and its clinical expression follows a stereotyped and predictable course in most cases. The absence of dystrophin in skeletal, cardiac, and brain muscle is responsible for the main manifestations of the disease.The first motor signs usually manifest before the age of 3, such as walking delay, frequent falls or walking on tiptoes. This muscular weakness progresses gradually until the loss of walking occurs in adolescence, with a mean age of 9.5 years according to previous studies [15].
Regarding the clinical findings of this population, it is essential to determine if the distribution of weakness is predominantly proximal, distal or generalized; it is also useful to identify factors that worsen or help with the primary symptoms, including hypotonia being a clinically significant finding in the examination of children with neuromuscular disorders.Several studies have confirmed that this variable is central and represents more than 80% of the cases analyzed [40], furthermore, Silvestri [41] points out in his research that hypotonia remains the most common reason for referring children to the pediatric electrodiagnostics laboratory, considering that muscle weakness is a common feature in many neuromuscular disorders. In our study, all patients confirmed with Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy (DMD) had a history of hypotonia.
In terms of the presence of falls, difficulty running, climbing stairs, standing up, walking on tiptoes, calf hypertrophy, Gowers sign, hyporeflexia, and decreased strength were observed in all patients diagnosed with Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy (DMD), data that are supported by previous studies such as Camacho A. et al. 2014 [29].The consideration of these parameters is essential when evaluating patients, as they reflect fundamental aspects of disease progression and impairment, allowing for more precise monitoring and early intervention to improve patients' quality of life.
Furthermore, the absence of data on scoliosis in the findings suggests that precise data cannot be determined. Scoliosis in patients with Duchenne muscular dystrophy (DMD) is progressive and often requires surgical treatment. As indicated by Dabaj et al. (2021), scoliosis and other spine deformities, along with their surgical and non-surgical treatments, the onset of bone fractures, other orthopedic surgeries, and mobility are essential elements for diagnosis and treatment. The lack of accurate information on these aspects hinders a comprehensive understanding and proper approach to scoliosis in these patients.
Regarding cognitive and neurodevelopmental impairment, this deterioration, apparently independent of motor impairment, is recognized as a characteristic in approximately one-third of DMD patients, as discussed by Alessandro et al. in their research [22], and delayed global development or language development may constitute an early sign of this impairment [39]. In our study, it was observed that 54.5% of confirmed patients had cognitive disorder, which represents 23.7% of the total patients. Additionally, it was found that 54.5% of confirmed patients also had a diagnosis of Attention Deficit Hyperactivity Disorder (ADHD).
The history of family members with DMD and consanguinity serve as a warning for primary care physicians, so this should always be investigated in cases of hypotonic children [7]. In our study of medical records evaluated for DMD, 88.2% of the patients described having a family history, in contrast Li et al., 2015 reports 23.1% of affected relatives in the family for DMD, hence considering family history is essential for early detection and diagnosis in order to conduct a comprehensive evaluation and transdisciplinary management, allowing for more personalized medical care focused on the specific needs of each patient and their family.
Regarding laboratory findings, Salas et al. 2014 describes an elevation of creatine kinase (CK) 10-100 times above its normal value from birth, a finding present in all patients with confirmed DMD diagnosis representing 93.4% of the total evaluated patients. Additionally, an elevation of aminotransferases (alanine aminotransferase and aspartate aminotransferase) was observed in all confirmed patients, supported by data from Birnkrant D. et al.2020 [20] and the study by Avaria María de los Ángeles et al.2012 [38], where it is concluded that children with Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy present an increase in the enzymes aspartate aminotransferase (AST) and alanine aminotransferase (ALT), which are mainly liver enzymes but are also present in skeletal muscle.
Findings in electrophysiological tests in confirmed patients were reported, including non-inflammatory myopathy in 9/22 patients, muscle fiber injury in 3/22 patients, myopathic pattern in 2/22 patients, and in one case, muscular dystrophy was identified. However, it is important to note that electromyography is not able to discriminate the type of myopathy, as pointed out by Salas, A.C. in his 2014 study [15].Pathological study through muscle biopsy, despite being an invasive test, is relevant for the management of patients with muscle fiber compromise and indicated as part of the primary approach in patients with progressive symmetrical dominant proximal weakness. This is supported by studies such as the ones conducted by Hwang, et al 2017 [37] and not performed in the majority of patients included in the study. Early and accurate diagnosis of the disease is an essential part of an effective management strategy, as treatment guidelines and prevention through counseling should be initiated as soon as possible, especially because there are now therapies available for a subset of patients.
Regarding molecular genetic testing, Salas, A. C.2014 [15], points out that it is preferable to start the analysis with this type of tests, as they are less invasive and considered the standard and most reliable way to diagnose neuromuscular diseases. These tests can confirm the diagnosis of Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy (DMD), which facilitates precise genetic counseling [39]. In our study, we found that out of 9/22 confirmed patients, they had the report of these tests but with incomplete records. Of these, 5/9 had undergone whole exome sequencing, 3/9 had undergone Multiplex Ligation-dependent Probe Amplification (MLPA) technique, and 1/9 had undergone sequencing of the DMD gene.
In general, the most common variants are deletions, as indicated by Aartsma-Rus A et al.2016 [5], indicate that Duchenne muscular dystrophy (DMD) is caused by mutations in the DMD gene that encodes dystrophin, highlighting large deletions and duplications as the most common, although small mutations have also been identified. This same pattern was observed by Eslava Otálora et al. in 2016 [16], who recorded deletions in 69.73% of the patients. In our study, we found deletions in 55.5% of the patients confirmed through molecular analysis in their medical records as follows: of the 9 patients with confirmed deletions, 2 had deletions in exons 45-52, another 2 in exons 46-55, and 1 patient had a deletion in exons 48-50. It is important to mention that there were no records of deletions in the medical history of 13 out of the total 22 confirmed patients.
The different variables described in the analysis of the results emphasize that paraclinical studies are an extension of the physical examination and help guide additional diagnostic studies, such as molecular genetic studies and muscle and nerve biopsies, as expressed by Mallik and Wei [24]. All diagnostic information should be interpreted not in isolation, but within the context of relevant historical information, family history, physical examination findings, and laboratory data, which should be systematically and clearly documented in medical records to record all patient information. This translates into the clinical information of patients with neuromuscular diseases being of vital importance in establishing treatments and clinical follow-up.It is crucial to highlight the importance of keeping thorough records in medical histories, given the continuous emergence of new therapeutic options, these records not only enable the offering of specific therapies, but also the adaptation of treatments as new therapeutic alternatives arise, therefore, an accurate diagnosis requires the active participation of families and patients, facilitating the early identification of symptoms and opening opportunities for possible treatments, especially in the context of the advancement of innovative therapies. In the case of degenerative and progressive neuromuscular diseases, such as Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy (DMD), informing families about the available treatment options is fundamental, a recent example is the approval by the FDA of a new drug, Duvyzat-givinostat, an oral medication for patients aged 6 or older with DMD [25].
On the other hand, Spinal Muscular Atrophy (SMA) is a hereditary disease that affects the cells of the anterior horn of the spinal cord, causing progressive weakness in the proximal muscles, as detailed by Schorling et al. This condition, with autosomal recessive inheritance, affects both men and women equally, requiring the presence of two copies of the gene, one from each parent, for its manifestation; the probability that these parents will have an affected child is 25% in each pregnancy. The estimated prevalence of SMA is around 1 case per 10,000 newborns. In Colombia, the scarcity of published studies on this disease and the lack of widespread awareness to conduct carrier studies at the population level, especially in rare diseases, hinder the obtaining of accurate statistics on its incidence and prevalence.
In our study, we observed that the onset of symptoms of Spinal Muscular Atrophy (SMA) occurred at 28.9 ± 37.7 months. These data vary depending on the clinical classification, which is divided into five subtypes based on age of onset and severity, as detailed in the study by Cardona et al., 2022 [26]. According to their research, the age in months for SMA type I was 1 month, for SMA type II was 9 months, and for SMA type III was 30 months. Additionally, regarding age at diagnosis, Franco Toñánez et al., 2021 [27] indicate a median age at clinical and genetic diagnosis of 6 months, while Urrutia-Osorio et al., 2020 [11] report an average age at diagnosis of 30.81 months, with a median of 23 months, and a range from 2 to 108 months. In contrast, in our study, we found an age at diagnosis of 37.9 ± 38.2 months.The variation in age at diagnosis can be attributed to several factors, such as tolerance for delays in developmental milestones, lack of knowledge about the disease, lack of timely access to specialist evaluations, and delays in diagnostic testing. These deficiencies are characteristic of our healthcare system and suggest that the onset of symptoms may occur even earlier, highlighting the importance of continuing to work on early detection of signs and symptoms of these diseases, especially in monitoring psychomotor development.
Regarding the gender of the patients analyzed, SMA had a greater impact on the female gender representing 66.6% of confirmed patients and 69.6% of the total patients. Ar Rochmah, et al, [28] reports that in their study, there were no significant gender differences in the number of patients with SMA type 1 or 2, and Urrutia-Osorio et al., 2020 [11] reports that there is a predominance in the incidence of spinal muscular atrophy in male patients. A study, carried out in mouse models, suggests that the intracellular antigen restricted to T-1 cells (TIA1), which regulates the splicing of exon 7 in spinal muscular atrophy, could be a gender-specific disease modifier [30].
When analyzing socioeconomic aspects, social security coverage, geographic location, and educational level, considering barriers to accessing medical care in certain areas of the country, we decided to evaluate distribution based on the country of birth instead of the place of medical care. We found that all patients with confirmed diagnoses belonged to the Low Stratum (Stratum 2), representing 100% of cases and covering 91%.3% of the total patients, also, all confirmed patients were affiliated with the subsidized regime, which represents 99% of the total patients. Additionally, 77.7% of confirmed patients and 56.5% of the total came from rural areas, and 77.7% of confirmed patients, along with 65.2% of the total, were not enrolled in school. There are no publications of studies in the Colombian population that report case series with these characteristics, only isolated case reports were found. It is possible that it is an underdiagnosed and poorly informed disease in Colombian literature.
In relation to the clinical findings in this population, it is crucial to determine if weakness mainly manifests proximally, distally, or generalized.Additionally, it is useful to identify factors that may exacerbate or alleviate the primary symptoms; for example, a history of muscle spasms could indicate fasciculations, while tremor or balance issues could be related to distal weakness or overlapping cerebellar involvement [26].
In our study, we observed that 73.9% of all patients experienced falls, while 3/9 confirmed SMA patients presented this symptom. Furthermore, 78.3% of all patients and 4/9 confirmed patients showed gait difficulties. Regarding difficulty running, 60.9% of all patients experienced it, although specific data for confirmed patients were not obtained. Difficulty climbing stairs affected 47.8% of the complete sample and 5/9 confirmed patients, while difficulty standing up was reported in 65%.2% of all patients and in 5/9 confirmed patients, the decrease in muscle strength was evident in all patients, while fasciculations were described in 91.3% of all patients and in all confirmed cases. Finally, areflexia was present in all confirmed patients, representing 65.2% of the total sample.
In contrast, Urrutia-Osorio et al., 2020 [11] reported lingual fasciculations in 86.7% for SMA type I, 46.2% for SMA type II, but it should be noted that lingual fasciculations can be observed in other conditions: hypoxic-ischemic injury, Moebius syndrome, Pompe disease, and bulbomedullary compression [31,32].
Spinal muscular atrophy (SMA) is one of the main causes of peripheral hypotonia, as described by Suárez et al., in 2018 [33]. In our study, we found a history of hypotonia in 95%.7% of all evaluated patients, including all confirmed patients with SMA. This finding is consistent with the study by Franco Toñánez et al., in 2021 [27], which also notes that hypotonia is one of the most common symptoms and a frequent reason for consultation in children with SMA, and with Valencia et al., 2015 [34] where they report hypotonia in 100% of patients.
Regarding cognitive function, this finding is not described in 78.3% of the total patients; likewise, there are no recorded data in confirmed patients. However, when observing these physical limitations imposed by the disease, it is important to emphasize that SMA does not affect the learning ability and intelligence of these individuals, that is, cognitive function is preserved. However, although there is no direct implication on cognitive function, deprivation of stimuli and contact with the environment can affect the development of language and learning in patients [35].
The presence of a family history of spinal muscular atrophy is an important sign that the primary care physician should take into account, especially when evaluating children with hypotonia. Cardona et al. 2022 reported that 21.4% of patients with SMA had affected family members; in contrast, our study found that 21.7% of all patients had a family history of SMA. A study conducted in Medellín revealed that 13.7% of patients had affected family members. This finding is relevant because spinal muscular atrophy is one of the most common autosomal recessive diseases, highlighting the importance of offering genetic counseling to the relatives of affected children.
Regarding laboratory findings, creatine kinase (CK) is usually found within normal limits or slightly elevated, reaching 2 to 4 times above the normal value, as detailed in the study by Urrutia-Osorio et al., in 2020. In our study, we observed that 21.7% of total patients and 5 out of 9 confirmed patients had a mild elevation in CK (< 400 IU/L), a finding that has also been reported by authors such as Ramos-Aguirre M. C. et al. in 2017. No records of elevated aminotransferases were found in the review of medical histories.
Although genetic tests are widely available, electromyography (EMG) continues to be used in many cases due to its widespread accessibility. In most cases, EMG reports a neurogenic denervation pattern, as reported by Franco Toñánez et al. in 2021.In our study, we found reports of denervation, polyneuropathy with axonal damage, and motor neuron disease, representing 3/23 patients (12.9% of the total cases), and in 3/9 confirmed patients.
Pathological study through muscle biopsy was not performed in most of the patients included in the study, despite being indicated as part of the primary approach in patients with dominant progressive symmetrical proximal weakness. This approach is supported by studies such as those conducted by Hwang et al. [37]. Early and accurate diagnosis of the disease is essential for an effective management strategy, as care guidelines and prevention through counseling should be initiated as soon as possible, especially now that therapies are available for a subset of patients.
Molecular genetic testing is the most reliable way to diagnose neuromuscular diseases, as supported by research conducted in Egypt by Hassan and colleagues [42]. According to this study, these tests can confirm the disease in approximately 94% of cases of Spinal Muscular Atrophy (SMA). The importance of early molecular diagnostics lies in the ability to manage patient care effectively, as SMA has a narrow therapeutic window.
In our study, we found that out of the 9 confirmed patients, 3 of them had molecular testing done using Multiplex Ligation-dependent Probe Amplification (MLPA). However, the reports obtained from these tests were incomplete, which prevented a comprehensive evaluation of the results.Regarding the other 6 confirmed patients, no detailed information about the molecular test performed was recorded. Instead of a detailed test report, a general description of the diagnosis confirmation was provided, without specifying the details of the technique used or the specific results obtained.
Spinal Muscular Atrophy (SMA) is mainly caused by homozygous deletions in the SMN1 gene, which account for approximately 95% of cases, as noted by Castiglioni et al. [3]. In comparison to these findings, the diagnosis of SMA is guided by the guidelines proposed by Kariyawasam et al., which include a comprehensive analysis of a history of motor difficulties, proximal muscle weakness, reduced or absent deep tendon reflexes, and evidence of motor unit disease.Furthermore, the identification of pathogenic biallelic variants in the SMN1 gene through molecular analysis, along with specific testing and evaluation of an increase in the number of copies of SMN2, is required, which may influence the phenotype of the disease [43]. These strategies provide a more solid approach for the diagnosis and monitoring of patients with SMA.
Lastly, it is crucial to develop the ability to differentiate between Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy (DMD) and Spinal Muscular Atrophy (SMA), as they present notable differences in both clinical and paraclinical aspects. DMD is characterized by progressive muscle weakness, cardiopulmonary complications, a higher incidence in males due to X-linked inheritance, significant elevations in creatine kinase (CK), and variants in the DMD gene that affect dystrophin production.On the other hand, AME presents with weakness and predominant muscle atrophy, especially in the motor neurons of the spinal cord and brainstem, and is characterized by the frequent presence of fasciculations, attributable to variants in the SMN1 gene that affect the survival of motor neurons. This differentiation is essential for accurate diagnostic evaluation and the formulation of specific therapeutic strategies for each disease, contributing to optimize clinical outcomes and the quality of life of patients.
CONCLUSIONS
This study constitutes the first retrospective, observational cross-sectional analysis of the search and characterization of pediatric patients with suspicion and/or diagnosis of AME and DMD through related ICD-10 codes. It represents the first documented registry in the southwest of Colombia and in the institution where the data was collected during the period from 2015 to 2021.
Neuromuscular diseases are showing an increase in their prevalence, suggesting the need for greater attention and resources to address this public health problem in Latin American countries. These diseases, of genetic origin, could benefit from screening programs for early detection and effective management. Unfortunately, in most countries in the region, the lack of screening programs limits the ability to identify and diagnose these conditions at early stages.
Timely diagnosis of neuromuscular diseases can have a significant impact on the prognosis and quality of life of patients, as it allows access to appropriate and timely treatment options. However, the follow-up of these patients can be difficult due to barriers to access to the healthcare system, including a lack of trained specialists and adequate resources. Additionally, the lack of patient re-contact to offer them advanced therapeutic options and cutting-edge diagnostic tests highlights the need to improve healthcare systems and patient follow-up.
The lack of a complete and updated registry of patients with neuromuscular diseases in robust databases also represents a challenge for research and health policy planning in the region, so it is crucial to have a complete record of all the information of each patient in systematized medical records, in this case, including the detailed study of the genetic variants found as this information is essential to guide treatment towards new therapies related to the identified variants (hyperpersonalized medicine). The availability of accurate and updated data allows for more precise and targeted medical care, thus optimizing therapeutic outcomes and improving the quality of life of patients affected by these variants.It is imperative to continue advancing in the integration and analysis of molecular data to drive the development of more specific and efficient therapies in the field of medicine.
Finally, knowledge of pathologies such as Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy (DMD) and Spinal Muscular Atrophy (SMA) is crucial for healthcare professionals in several aspects. Firstly, by understanding the differences in signs and symptoms between these diseases, doctors can diagnose more accurately and early, allowing for appropriate interventions and treatments to be initiated at critical stages. Secondly, detailed knowledge of these conditions is essential for long-term care planning and management of potential complications. Additionally, access to updated information on SMA and DMD allows healthcare professionals to educate patients and their families, search for carriers, or other affected individuals in the family, as well as provide emotional and psychological support, ensuring comprehensive and personalized care.In summary, mastery of these pathologies by healthcare professionals is essential to improve clinical outcomes and impact on quality of life, morbidity, and mortality attributed to these pathologies.
ETHICAL CONSIDERATIONS
The research protocol was presented and approved by the following instances: the Pediatric Research Group GRINPED, as per act N.48, and the Ethics Committee of the institution where the study was conducted, as per act N.257.
This research project, approached from a perspective of reviewing medical records, aims to provide results that can benefit the General Health Systems and implement management and public action strategies, minimizing any potential risks. Respect for the rights of the authors is guaranteed by adequate citation of each research according to established norms.It is important to note that the study did not involve the use of human or animal population, as the methodology did not require it. Therefore, the collected information was used exclusively to achieve the project's objectives, maintaining anonymity to protect the privacy of the patients involved.
Furthermore, strict clinical practice standards and ethical principles were followed in the development of this project. At this point, Resolution 2626, of September 2012, is issued, modifying the Comprehensive Health Care Policy-PAIS and adopting the Comprehensive Territorial Action Model (MAITE), which focuses on individuals, families, and communities, to ensure effective social and community participation through the coordination of different agents and users, in addition to territorial synchronization of Departments, districts, and municipalities.On the other hand, as established in Resolution 8430 of 1993, in Article 11, this study is classified as: Study without risk. In this sense, these are studies that use retrospective documentary research techniques and methods in which there is no intentional intervention or modification of biological, physiological, psychological, or social variables in the study participants, since, in this case, it is about the medical records of patients with suspected and/or diagnosed DMD and SMA with permission to view records and carry out documentary research.
UNIVERSAL BIOETHICAL PRINCIPLES
Referring to those general judgments that serve as a basic justification for the many ethical prescriptions and particular evaluations of human actions.In this research, the relevance of applying the bioethical-universal principles of Autonomy, beneficence, non-maleficence, and justice will be taken into account in order to contribute to the scientific community and society in general.
BELMONT REPORT
The National Commission met and in 1979 published the Belmont Report. The principles developed and subsequently presented in the Belmont Report have been considered fundamental and widely adopted in research ethics, therefore this statement impacts the distinction between research and practice, a discussion about the three basic ethical principles and observations associated with these principles.The term "practice" refers to interventions aimed at increasing the well-being of an individual patient with reasonable expectations of success that generate benefits or contributions to knowledge; the objective of medical practice is to offer and guarantee the identification of risk factors in order to establish a preventive treatment or early and appropriate diagnosis for the subsequent implementation of therapeutic treatment associated with the pathology detected in the patient, integrally, the term "research" denotes an activity aimed at verifying one or more hypotheses that allow the development of conclusions, thus contributing to the acquisition of generalizable knowledge; research is described in a formal protocol that presents a general objective and a set of procedures designed to achieve this objective.Taking into account the above, for the present project, the Principles and Ethical Guidelines for the Protection of Human Subjects in Research are considered for the definition of methodology and achievement of objectives of this research.
Acknowledgements
To all the people who contributed to the monitoring and development of the study.
About the authors
TMJM is a pediatric resident at Universidad Libre - Seccional Cali. MAGA is a pediatrician with a master's degree in epidemiology, and a postgraduate teacher at the Faculty of Health, Universidad Libre Seccional Cali. LJMG is a pediatrician with a master's and doctorate in medical genetics, and a postgraduate teacher at the Faculty of Health, Universidad Libre Seccional Cali.
References
[1] Ayuso C. Enfermedades raras. [Online].; 2023. Available from: https://newsrare.es/wp-content/uploads/2023/05/nR-14-Vol-8-num-1-2023-WEB-OPT.pdf.
[2] Martínez Carrasco C, et al. Enfermedad neuromuscular: evaluación clínica y seguimiento desde el punto de vista neumológico. An Pediatr (Barc). 2014. http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.anpedi.2014.02.024
[3] Castiglioni C, Lozano-Arango A. Atrofias musculares espinales no asociadas a SMN1Spinal muscular atrophies not associated with the SMN1 gene. [Online].; 2018. Available from: https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S0716864018301214.
[4] Osorio A, Ortez C. 50 preguntas sobre la DMD. [Online].; 2021 [cited 2023. Available from: https://ptccampus.es/downloads/dmd/Distrofia-muscular-Duchenne-preguntas-clave.pdf.
[5] Aartsma-Rus A, Ginjaar I, Bushby K. The importance of genetic diagnosis for Duchenne muscular dystrophy.. [Online].; 2016 [cited 2023 J Med Genet. 2016 Mar;53(3):145-51.. Epub 2016 Jan 11. PMID: 26754139; PMCID: PMC4789806. Available from: doi: 10.1136/jmedgenet-2015-103387.
[6] Muñoz R., Castellar S., Ruiz E., et al. Consenso colombiano para el seguimiento de pacientes con Distrofia muscular de Duchenne. [Online].; 2019. Available from: https://revistapediatria.org/rp/article/download/153/99/1442.
[7] León López, Osvaldo M (2019). Bases bioquímicas, fenómenos e interferencias biológicas de la Distrofia muscular de Duchenne. figshare. Journal contribution. https://doi.org/10.6084/m9.figshare.8020757.v1
[8] Akat A, Karaöz E. Cell Therapy Strategies on Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy: A Systematic Review of Clinical Applications. Stem Cell Rev Rep. 2024 Jan;20(1):138-158. doi: 10.1007/s12015-023-10653-8. Epub 2023 Nov 13. PMID: 37955832.
[9] Saad FA, Saad JF, Siciliano G, Merlini L, Angelini C. Duchenne Muscular Dystrophy Gene Therapy. Curr Gene Ther. 2024;24(1):17-28. doi: 10.2174/1566523223666221118160932. PMID: 36411557.
[10] Schorling D, Pechmann A, Kirschner J. Advances in Treatment of Spinal Muscular Atrophy - New Phenotypes, New Challenges, New Implications for Care. [Online].; 2020. Available from: doi: 10.3233/JND-190424.
[11] Urrutia-Osorio ME, Ruiz-García M. Demographic and clinical profile in patients with spinal muscular atrophy: Series of 31 patients. Acta Pediatr Mex. 2020;41:47-57
[12] Abreu N. Overview of Gene Therapy in Spinal Muscular Atrophy and. [Online].; 2020. Available from: https://d197for5662m48.cloudfront.net/documents/publicationstatus/41279/preprint_pdf/cd742da19a65469eb28fe98c09bc7a9e.pdf.
[13] Cattinari MG, de Lemus M, Tizzano E. RegistrAME: the Spanish self-reported patient registry of spinal muscular atrophy. Orphanet J Rare Dis. 2024 Feb 19;19(1):76. doi: 10.1186/s13023-024-03071-7. PMID: 38373977; PMCID: PMC10877841.
[14] Crisafulli S, Sultana J, Fontana A. Global epidemiology of Duchenne muscular dystrophy: an updated systematic review and meta-analysis. [Online].; 2020. Available from: https://doi.org/10.1186/s13023-020-01430-8.
[15] Salas, A. C. (2014). Distrofia muscular de Duchenne. Anales de Pediatría Continuada, 12(2), 47–54. doi:10.1016/s1696-2818(14)70168-4
[16] Eslava Otálora, Andrea Cecilia, Registro de pacientes con distrofinopatías en Colombia,2016-08-17, https://repository.urosario.edu.co/server/api/core/bitstreams/a7d766f9-f6d7-4eca-ac17-b3be88ee33f9/content
[17] Li, X., Zhao, L., Zhou, S., Hu, C., Shi, Y., Shi, W., … Wang, Y. (2015). A comprehensive database of Duchenne and Becker muscular dystrophy patients (0–18 years old) in East China. Orphanet Journal of Rare Diseases, 10(1), 5. http://doi.org/10.1186/s13023-014- 0220-7
[18] Nascimento A, Medina J, Camacho A, Madruga M, Vilchez J. Consenso para el diagnóstico, tratamiento y seguimiento del paciente con distrofia muscular de Duchenne. [Online].; 2019. Available from: https://pesquisa.bvsalud.org/portal/resource/pt/ibc-186349.
[19] Rangel, V., Martin, A. S., & Peay, H. L. (2012, January). DuchenneConnect Registry Report. PLoS Currents. http://doi.org/10.1371/currents.RRN1309
[20] Birnkrant D, Bushby K, Bann C, Apkon S, Blackwell A BDCLCPHSPSSNTJWKWLWD. DMD Care Considerations Working Group. Diagnosis and management of Duchenne muscular dy. [Online].; 2020. Available from: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/29395989/.
[21] Dabaj I, Ferey J,MFea. Muscle metabolic remodelling patterns in Duchenne muscular dystrophy revealed by ultra-high-resolution mass spectrometry imaging. [Online].; 2021. Available from: https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-021-81090-1.
[22] D'Alessandro R, Ragusa N, Vacchetti M, Rolle E, Rossi F, Brusa C. Assessing Cognitive Function in Neuromuscular Diseases: A Pilot Study in a Sample of Children and Adolescents. [Online].; 2021. Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC8537027/.
[23] Cadena D. Encefalitis de Rasmussen. [Online].; 2019. Available from: https://revistas.fucsalud.edu.co/index.php/repertorio/issue/download/76/2019-05-01.PDF.
[24] Mallik A, Wei I. Nerve conduction studies: Essentials and pitfalls in practice. [Online].; 2005. Available from: 10.1136/jnnp.2005.069138.
[25] Tolosa A. La FDA aprueba un fármaco para el tratamiento de la Distrofia Muscular de Duchenne. [Online].; 2024. Available from: https://genotipia.com/genetica_medica_news/duvyzat-farmaco-para-el-tratamiento-de-la-distrofia-muscular-de-duchenne/?utm_source=NL%20Genotipia%202023&utm_medium=email&utm_campaign=Genotipia%20Hoy%2030%20Marzo%202024%20%2801HT2X8A8F29JTQ3JD890G0WG5%29&_kx=.
[26] Cardona N OSEJMMPG. Clinical-functional characterization of patients with spinal muscular atrophy in Central-Western Colombia. [Online].; 2022 [cited 2023. Available from: doi: 10.7705/biomedica.6178.
[27] Franco Toñánez Carlos, Godoy Sánchez Laura, Casartelli Galeano Marco. Caracterización clínica, epidemiológica y genética de pacientes con atrofia muscular espinal: serie de 26 pacientes pediátricos. Pediatra. (Asunción) [Internet]. Abril de 2021; Disponible en: http://scielo.iics.una.py/scielo.php?script=sci_arttext&pid=S1683-98032021000100044&lng=en. https://doi.org/10.31698/ped.48012021008.
[28] Ar Rochmah M, Shima A, Harahap N, Niba E, Morisada N, Yanagisawa S, et al. Gender Effects on the Clinical Phenotype in Japanese Patients with Spinal Muscular Atrophy.. [Online].; 2018. Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5826018/.
[29] Camacho A. Distrofia muscular de Duchenne. [Online].; 2014. Available from: https://www.elsevier.es/index.php?p=revista&pRevista=pdf-simple&pii=S1696281814701684&r=51.
[30] Howell MD, et al. TIA1 is a gender-specific disease modifier of a mild mouse model of spinal muscular atrophy. Nat Sci reports 2017; 7 (1): 7183. https://doi.org/10.1038/ s41598-017-07468-2
[31] Lunn MR, Wang CH. Spinal muscular atrophy. Lancet. 2008;371(9630):2120-33. doi: 10.1016/S0140- 6736(08)60921-6.
[32] Simone C, et al. Is spinal muscular atrophy a disease of the motor neurons only: Pathogenesis and therapeutic implications? Cell Mol Life Sci 2016; 73 (5): 1003-20. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00018-015-2106-9
[33] Suárez, Bernardita; Araya, Gabriela (2018). Síndrome hipotónico como manifestación de enfermedad neuromuscular hereditaria en la infancia. Revista Médica Clínica Las Condes, 29(5), 502–511. doi:10.1016/j.rmclc.2018.07.003
[34] Valencia HD, Rendón Muñoz J, Pineda N, Ortiz B, Montoya JH, Cornejo JW. Características clínicas de los pacientes menores de 18 años con atrofia muscular espinal en Medellín, 2008 - 2013. Acta Neurol Colomb. 2015;32: 9-17. https://doi.org/10.22379/2422402270
[35] Von Gontard A, Zerres K, Backes M, et al. Intelligence and cognitive function in children and adolescents with spinal muscular atrophy. Neuromuscul Disord. 2002;12(2):130-136.
[36] Ramos-Aguirre M. C. (2017). Atrofia muscular espinal. Revista Acta de Ciencia en Salud. 3(1): p. 39-52. file:///C:/Users/Asus/Downloads/Ramos-Aguirre+Miroslava,+Atrofia+muscular+espinal.pdf
[37] Hwang H, Lee J, Choi Y. Clinical Characteristics of Spinal Muscular Atrophy in Korea Confirmed by Genetic Analysis. [Online].; 2017. Available from: doi: 10.3349/ymj.2017.58.5.1051.
[38] Avaria María de los Ángeles, Beytía María de los Ángeles, Kleinsteuber Karin, Rodillo Eliana, Alegría Sylvia. Aumento de transaminasas: una manifestación de distrofia muscular de Duchenne. Rev. chil. pediatr. [Internet]. 2012 Jun Disponible en: http://www.scielo.cl/scielo.php?script=sci_arttext&pid=S0370-41062012000300007&lng=es. http://dx.doi.org/10.4067/S037041062012000300007
[39] Prior-de Castro C, Gómez-González C, Rodríguez-López R, Macher H. Diagnóstico genético prenatal de enfermedades monogénicas. [Online].; 2021. Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC10197186/.
[40] Erazo R. Niños con hipotonía muscular: la clave es un diagnóstico precoz. [Online].; 2019. Available from: https://www.clinicaalemana.cl/articulos/detalle/2019/ninos-con-hipotonia-muscular-la-clave-es-un-diagnostico-precoz.
[41] Silvestri N. Muscle and Neuromuscular Junction Disorder). [Online].; 2022. Available from: https://journals.lww.com/continuum/fulltext/2022/12000/key_points_for_issue.23.aspx.
[42] Hassan H, Fahmy N, El-Bagoury N. MLPA analysis for molecular diagnosis of spinal muscular atrophy and correlation of 5q13.2 genes with disease phenotype in Egyptian patients. [Online].; 2022. Available from: https://doi.org/10.1186/.
[43] Kariyawasam D, Carey K, Jones K, FM. New and developing therapies in spinal muscular atrophy. [Online].; 2018. Available from: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/29703692.


